Neutron Stars
14.10 - Understand the principal stages and timescales of stellar evolution for stars of much larger mass than the Sun, including:e) neutron star
There are two types of formation of a neutron star.
- A star between 4 and 25 solar masses will grow to a red super giant and explode as a supernova, leaving a neutron star smaller than the size of Earth.
- A white dwarf than cannot contain its mass through electron degeneracy pressure and exceeds 1.4 solar masses will become a neutron star
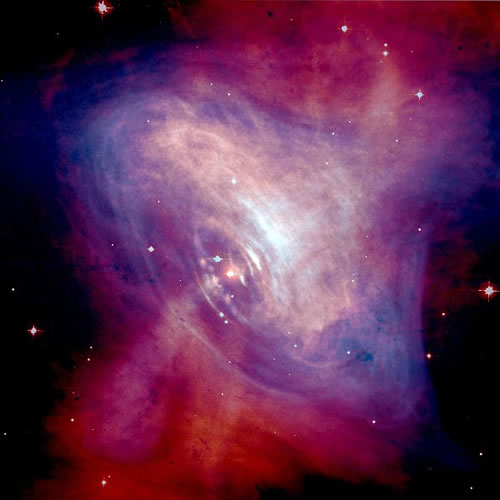
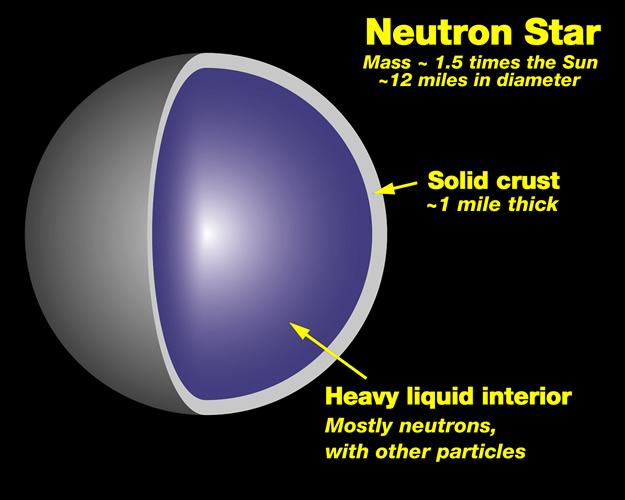
These stars are compressed so much that they are composed entirely of neutrons, parts of the atom without electrical charge. Electrons and protons combine to form neutrons.
This is the equivalent of the size of the Sun in the same area as a city or the human population on Earth fitting inside an area the size of a sugar cube.
Neutron stars rotate rapidly after formation, typically spinning between fractions of a second and half a minute. We can detect this because they emit radio pulses, and the ones we detect are known as pulsars. Radio astronomy has also detected brightness and temperature from neutron stars, and astronomers have used x-ray astronomy to detect them when matter from companion stars falls onto neutron stars.
Animation
Mix & Match
Questions
- Describe a neutron star
- What are they composed of?
- How do they 'act'? - What technques have scientists used to discover neutron stars
Did you know?
There are over 2000 known neutron stars that have been discovered in our galaxy.
Links
Imagine the Universe Neutron Stars

 | © All Rights Reserved |
| © All Rights Reserved |