Phases of the Moon
4.9 - Understand the lunar phase cycleWe are familiar with looking at the Moon and seeing it change shape. Sometimes it is a thin crescent, sometimes half full and totally full. As we observe the Moon from Earth it shows a repeated pattern of phases every month during its orbit. These are called the phases of the Moon.
All light from the Moon is reflected light from the Sun. As the Moon orbits the Earth, we see different amounts of sunlight reflected from its surface depending on its position relative to the Sun. If we observed the Moon from the Sun its surface would always be fully illuminated. No more than 50% of its surface can ever be lit at once.
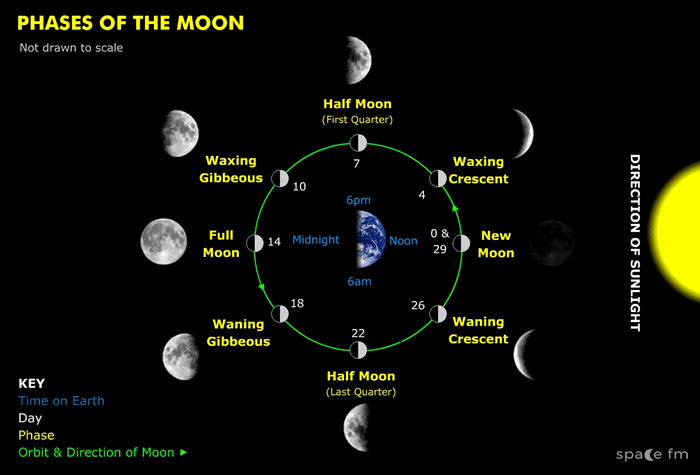
The new Moon marks the start of these phases. A new Moon is dark and difficult to see as it will appear near the sun in the daytime and not visible. This is because the Moon lies between the Sun and Earth and the unlit side is facing towards us.
Over the next seven days, more of the Moon is visible. The moon is said to be waxing. A crescent appears and the amount visible grows larger to a half moon. From the northern hemisphere of Earth, we see the right-hand side lit and the left-hand side dark. The reverse is true of all these phases if you were observing from the southern hemisphere.
Confusingly, the Moon is at the stage of its orbit called First Quarter as it is a quarter of the way around its orbit (even though it's half full). When it is half full it is said to be at ‘dichotomy’.
The moon takes another 7 days to become a full Moon when its entire surface is visible to us on Earth. This occurs when the Moon lies on the Opposite side of the Earth from the Sun.
Between a half moon and full moon, the Moon is said to show a gibbous phase. It is waxing gibbous. The term gibbous comes from the Italian word "giboso" which means "humpbacked".
The moon then starts to reverse these phases. It is said to be waning. Now the right-hand side darkens, and the left-hand side remains lit (from the northern hemisphere). It gets to the half moon (dichotomy) stage and is said to be at third quarter. It moves to become a waning crescent until it becomes a new moon once more.
Timings
We can usually tell when the Moon is visible in the sky by knowing what its phase is. When the Moon is new it appears near the sun and so rises and sets at the same time. A first-quarter (half-full waxing) moon can be seen from noon until midnight. A full moon is opposite the Sun and is visible from sunset until sunrise. When the full moon is at its highest point in the sky it is close to midnight local time. A third quarter moon (half-full waning) will be visible from midnight until moon.
Earth’s phases from the Moon
If you were observing the Earth from the Moon, you would see the Earth exhibit phases also. These would be the opposite of the Moon's phases. During a new Moon, the observer on the Moon would see a full Earth. There is evidence of this when the Moon is showing a crescent low in the sky after sunset. Sometimes we may see an outline of the remainder of the Moon. This effect is called 'Earthshine'. The full Earth is reflecting light back to the Moon. The Earth reflects more light back to the Moon than the Moon does to us for two reasons.
- The Earth is larger and covers a wider area of sky.
- The atmosphere, clouds, continents and seas visible from space act as efficient reflectors.
Sometimes the reflection of the full Earth reflects on the Moon when it is a crescent and we can see a faint outline of the whole Moon. This effect also has an old name of "The old Moon in the new Moon's arms".
Phases on other planets
Mercury and Venus also show phases similar to the Moon as they orbit the Sun closer than Earth. Mars can also be seen to show a gibbous phase when observed from Earth at certain times.
Animation
Summary
| Day | Phase |
|---|---|
| 0 | New Moon |
| 7 | Waxing Half Moon (1st quarter) |
| 14 | Full Moon |
| 22 | Waning Half Moon (3rd quarter) |
| 29 | New Moon |
Quarters? Halves?
You will see references to a first quarter and third quarter when referring to a half moon. This sounds illogical but a half moon is when the moon is at 90° (a quarter of a circle) to the Earth and Sun and so looks a half. First quarter is one quarter of the time through its orbit, third quarter is three quarters.
Questions
- Describe the phases of the Moon
- Explain why we see these phases
THE MOON TONIGHT
Interactive
Mix & Match
Did you know?
A waning crescent moon is sometimes known as a Decrescent moon
Links
- Time and Date Moon Phases
- Enchanted learning Information about phases
- Moon Phases Keith's Moon phases
- Fourmilab - Earth Viewer See the current phase of Earth from the Moon
- Bad Astronomy Moon Phases
 | © All Rights Reserved |
| © All Rights Reserved |